Energy management has become a top priority across industrial, commercial, and HVAC sectors. Rising energy prices, sustainability goals, and strict regulatory requirements are pushing companies to find ways to reduce heat loss, improve system performance, and extend equipment life. One highly effective—but often overlooked—solution is proper insulation cladding.
Many facilities invest in insulation but fail to protect it adequately. Without cladding, insulation deteriorates from moisture, UV exposure, mechanical impact, and corrosion. This gradually leads to energy loss and increased operational costs. This article explains how high-quality cladding plays a critical role in energy savings and long-term system efficiency.
Understanding the Link Between Cladding and Energy Efficiency
Insulation controls heat transfer, but cladding determines how long the insulation can perform. When insulation absorbs moisture or gets damaged, its thermal resistance drops dramatically. In many cases, insulation that is wet loses up to 50% of its effectiveness.
Cladding acts as the protective shield that keeps insulation dry, intact, and functional. Aluminium and stainless-steel jacketing are commonly used because they offer durability, corrosion resistance, and outstanding lifespan—even in extreme environments.
When the protective layer is properly installed, energy loss is reduced, and HVAC or industrial systems operate more efficiently.
Why Industries Lose Energy Without Proper Cladding
From chemical plants to refineries, energy-intensive operations rely on thermal insulation daily. However, studies show that a large portion of insulated systems develop hidden issues such as:
- Moisture intrusion
- Corrosion under insulation (CUI)
- Mechanical wear
- Vibration-related damage
- UV degradation
These factors compromise insulation performance and can increase heat loss by up to 10–20% annually. Over time, this translates into higher fuel or electricity consumption and unnecessary carbon emissions.
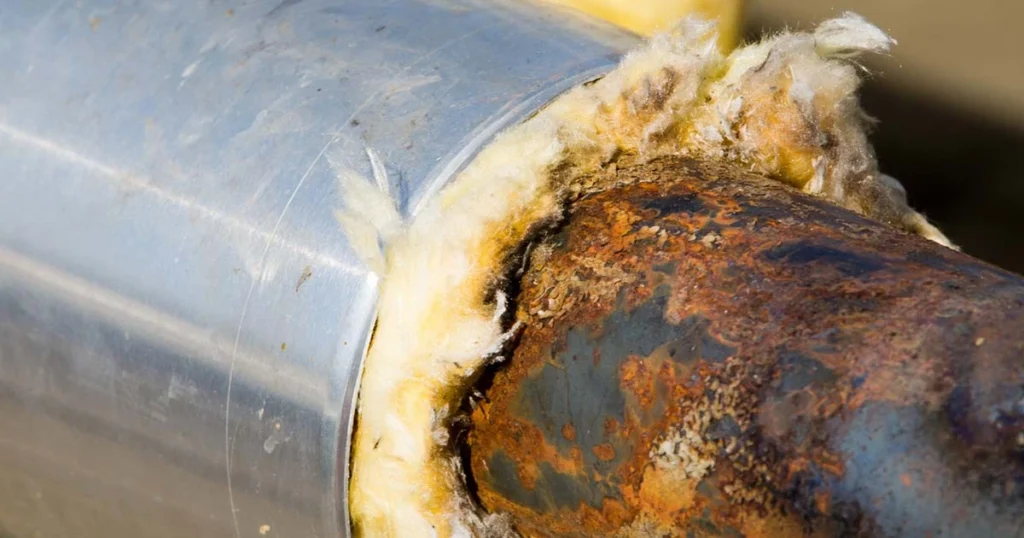

How Cladding Minimizes Heat Loss
1. Prevents Moisture Intrusion
Moisture is the biggest enemy of insulation. Once insulation becomes wet, its thermal value drops, and corrosion begins.
Aluminium jacketing with moisture barrier prevents this penetration and keeps insulation dry.
2. Maintains Thermal Resistance Over Time
Cladding protects insulation from external conditions, ensuring that the insulation retains its R-value for years.
3. Reduces Surface Temperature Fluctuations
Stable surface temperatures result in improved process control, reduced heating/cooling demand, and safer working environments.
4. Minimizes Air Leakage in HVAC Systems
Properly sealed cladding prevents air loss in ducts and chilled-water lines, improving HVAC efficiency.

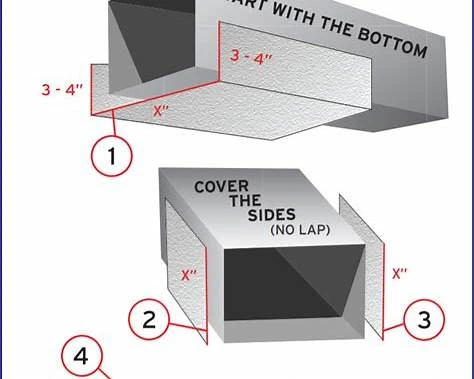
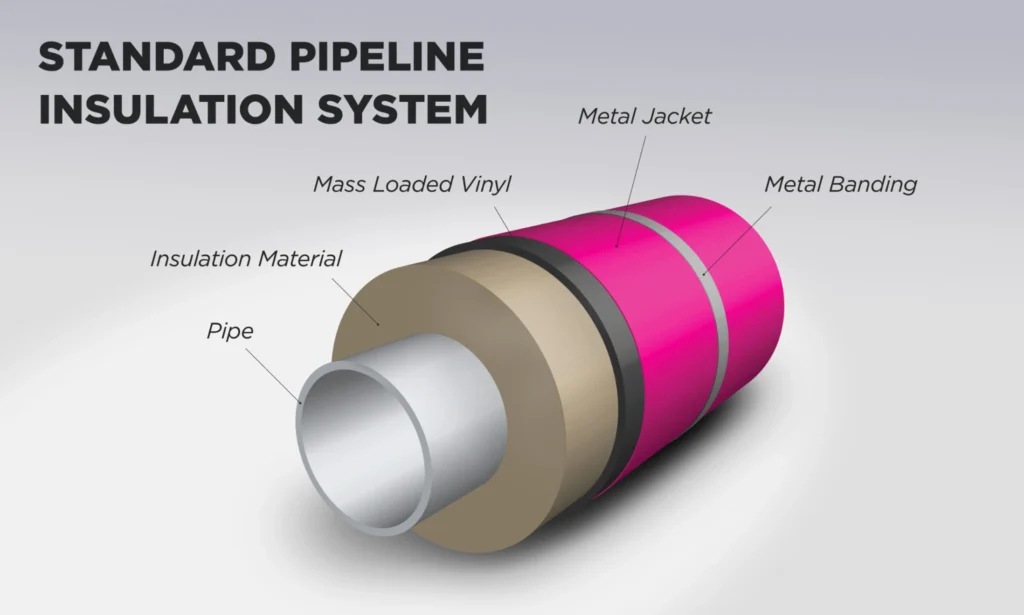
Cost Savings Achieved Through Proper Cladding
Lower Energy Bills
A well-protected insulation system reduces heat loss, cuts fuel consumption, and lowers cooling demand.
Reduced Maintenance
Systems with cladding require far less repair because insulation remains dry, clean, and secure.
Extended Equipment Life
Cladding protects steel tanks, pipes, and vessels from corrosion under insulation—one of the leading causes of industrial failures.
Better Regulatory Compliance
Industries must meet safety, energy, and environmental norms. Proper cladding supports compliance effortlessly.
Choosing the Right Material for Maximum Energy Efficiency
Aluminium Jacketing
- Lightweight
- High corrosion resistance
- Excellent reflectivity
- Ideal for coastal and humid regions
Stainless Steel Jacketing
- Superior strength
- High-temperature resistance
- Best suited for aggressive chemical environments
Both materials offer long-term performance, but the choice depends on operating temperature and environmental exposure.
Expert Tips for Improving Energy Performance Using Cladding
- Always use cladding with moisture barriers in coastal or chilled-water applications.
- Ensure there are no gaps or poorly sealed joints during installation.
- Conduct annual inspections to detect early damage.
- Replace worn-out bands, screws, and mastics immediately.
- Use pre-formed cladding sections for pipes to ensure accurate fitting.
Conclusion
Proper insulation cladding is one of the most cost-effective ways to enhance energy efficiency across industrial and HVAC systems. When installed and maintained correctly, it reduces heat loss, prevents corrosion, lowers energy bills, and delivers long-term performance.
For industries looking to improve operational efficiency and sustainability, investing in high-quality metal cladding is not just a best practice—it is a necessity.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is insulation cladding and why is it important?
Insulation cladding is the protective outer layer installed over insulation on pipes, ducts, tanks, and equipment. It protects insulation from moisture, corrosion, UV exposure, and mechanical damage, ensuring long-term thermal performance and energy efficiency.
2. How does cladding improve energy efficiency?
Cladding prevents insulation from getting wet or damaged. Dry, intact insulation maintains its thermal resistance (R-value), reducing heat loss, improving system efficiency, and lowering energy consumption in industrial and HVAC systems.
3. What happens if insulation is not protected with cladding?
Without cladding, insulation can absorb moisture, crack, or deteriorate. This can reduce insulation effectiveness by up to 50%, increase energy loss by 10–20% annually, and lead to corrosion under insulation (CUI), higher maintenance costs, and equipment failure.
4. Which cladding material is best for energy efficiency?
Both aluminium and stainless-steel cladding offer excellent energy-saving performance:
Aluminium cladding is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and ideal for HVAC, chilled water, and coastal environments.
Stainless-steel cladding provides superior strength and high-temperature resistance, making it suitable for chemical plants and aggressive industrial environments.
5. Can cladding help reduce operating costs?
Yes. Proper insulation cladding reduces heat loss, lowers fuel and electricity consumption, minimizes maintenance needs, and extends equipment life—resulting in significant long-term operating cost savings.
6. How does cladding prevent corrosion under insulation (CUI)?
Cladding acts as a moisture barrier, preventing water ingress that leads to corrosion. When installed with proper sealing and moisture barriers, cladding significantly reduces the risk of CUI in pipes, tanks, and vessels.
7. Is cladding necessary for HVAC systems?
Yes. In HVAC systems, cladding minimizes air leakage, stabilizes surface temperatures, protects insulation from damage, and improves overall system efficiency—especially in chilled-water and ducting applications.
8. How often should insulation cladding be inspected?
Annual inspections are recommended. Regular checks help identify loose bands, damaged jacketing, seal failures, or early corrosion, preventing costly repairs and energy losses.
9. Does insulation cladding help with regulatory compliance?
Yes. Proper cladding supports compliance with energy efficiency standards, safety regulations, and environmental requirements by reducing emissions, improving thermal control, and protecting equipment.
10. Is insulation cladding a long-term investment?
Absolutely. High-quality metal cladding delivers long service life, consistent energy savings, reduced downtime, and improved sustainability—making it one of the most cost-effective long-term investments for industrial and HVAC systems.

